Acquisition financing, or funding, pertains to the capital or resources that a company secures to undertake the acquisition or takeover of a target entity. It is crucial for companies to secure capital for acquiring target entities, driving domestic and cross-border deals. Multiple methods exist to secure such funds, contingent upon the nature of the acquisition.
The structure of acquisition finance varies depending on the geographical regions and borders. Acquisitions can be broadly classified into domestic and cross-border categories. Cross-border acquisitions are typically segmented into two: Inbound and Outbound acquisitions.
In recent times, notable acquisition transactions have occurred in India. In June 2023, Tata Communications announced its intention to acquire the US-based enterprise messaging firm Kaleyra for US$ 100 million in an all-cash deal (Outbound acquisition). Following this, in July 2023, the Indian arm of the French advertising and public relations company Havas revealed its acquisition of PivotRoots (Inbound acquisition). Additionally, in August 2023, the jewellery retailer Titan expanded its stake in CaratLane by acquiring an additional 27.18% for Rs. 4,621 crore (US$ 556.01 million) (Domestic acquisition). These instances highlight the dynamic landscape of acquisition activities, showcasing diverse sectors and moves within the Indian market.
Inbound acquisitions refer to instances where a foreign entity directly purchases a company incorporated in India or does so through foreign owned and controlled operating company (FOCC) incorporated in India as a subsidiary of an offshore entity
Outbound acquisitions refer to instances where an Indian acquirer directly purchases a company incorporated outside India or does so through a special purpose vehicle incorporated outside India.
Commonly, the financial options available for such types of acquisitions are summarised in below table:
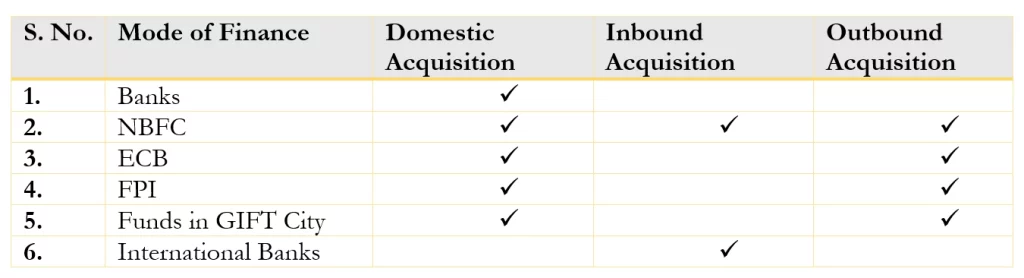
Disclaimer: The above table only outlines commonly used acquisition finance options based on our secondary research.
Some important factors that must be taken into account when domestic entities engage in different types of acquisitions are:
- For domestic acquisitions, the guidelines set forth by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) limit the capacity of Indian banks to provide financing for the acquisition of equity shares in an Indian company, except in exceptional circumstances.
- For outbound acquisition, acquiring entity has the option to secure loans from banks, financial institutions, and other lenders, provided it adheres to specific qualitative and quantitative regulatory constraints.
- Considering the limited availability of global funds for small to medium scale domestic companies, acquisition financing through GIFT City is facilitated by leveraging its status as an IFSC, which opens avenues for accessing global financial markets, engaging with international banks and investors, and utilizing a regulatory framework tailored for cross-border financial activities.
Adherence to regulatory frameworks established by the RBI and FEMA under FDI and ODI regulations is imperative for both Inbound and Outbound acquisitions. The RBI regulations play a crucial role in acquisition financing, and the introduction/ modification of any regulations hold the potential to usher in transformative changes in the acquisition financing landscape. This, in turn, may lead to heightened dynamism and structural shifts in the overall scenario.
In the face of elevated global inflation and economic uncertainties, Indian corporations with a solid foundation haves potential to sustain continued growth in domestic acquisitions. We believe that the need of the hour is to facilitate equity finance from Indian banks within the established regulations.



